Canada is one of the most diverse and multicultural countries in the world, with a population that continues to grow at a steady pace. The Canadian population has been a topic of interest for policymakers, researchers, and individuals alike. In this article, we will explore the demographics, growth patterns, and key factors influencing the population of Canada.
With a vast landscape and abundant natural resources, Canada attracts immigrants from all over the world. Its welcoming policies and high quality of life contribute significantly to its population growth. Understanding the dynamics of Canada's population is crucial for anyone interested in its economic, social, and cultural development.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of Canada's population, covering key aspects such as demographic trends, immigration patterns, age distribution, and regional variations. By the end of this guide, you will have a clearer picture of how Canada's population is shaping the nation's future.
Read also:Karen Swift Unveiling The Life And Legacy Through The Lens Of Documentary
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Canada Population
- Demographics of Canada
- Population Growth Trends
- Immigration and Its Role
- Age Distribution
- Regional Variation in Population
- Urbanization in Canada
- Economic Impact of Population Growth
- Challenges Facing Canada's Population
- Future Projections
Introduction to Canada Population
Canada's population stands as one of the most significant indicators of its progress and potential. According to Statistics Canada, the population has been steadily increasing, driven by both natural growth and immigration. The country's population growth is a testament to its appeal as a destination for immigrants and its ability to maintain a healthy birth rate.
Why Population Matters
Population figures are critical for understanding a country's economic strength, labor market dynamics, and social structure. For Canada, a growing population translates into a larger workforce, increased consumer base, and enhanced innovation. However, managing this growth requires careful planning and policy implementation.
Canada's population growth is influenced by several factors, including immigration policies, birth rates, and mortality rates. These elements work together to shape the demographic landscape of the nation.
Demographics of Canada
The demographics of Canada reveal a rich tapestry of diversity and multiculturalism. The country is home to people from various ethnic backgrounds, religions, and cultures. This diversity contributes to Canada's unique identity and its status as a global leader in inclusivity.
Read also:Brittany Zamora A Comprehensive Overview Of The Controversial Case
Ethnic Diversity
- Indigenous peoples make up approximately 4.9% of the population.
- European descent remains the largest ethnic group, primarily due to historical immigration patterns.
- Asian, African, and Caribbean communities have grown significantly in recent years, reflecting Canada's commitment to multiculturalism.
Data from the 2021 Census highlights that visible minorities now account for over 23% of the population, a figure expected to rise in the coming decades.
Population Growth Trends
Canada's population growth has been consistent over the years, averaging around 1% annually. This growth is primarily attributed to immigration, which accounts for approximately 80% of the increase. Natural growth, defined as the difference between births and deaths, contributes the remaining 20%.
Factors Influencing Growth
- Immigration: Canada's immigration policies are designed to attract skilled workers, family members, and refugees.
- Birth Rates: While birth rates have declined in recent years, they remain relatively stable compared to other developed nations.
- Mortality Rates: Advances in healthcare and technology have contributed to lower mortality rates, extending life expectancy.
According to the United Nations, Canada's population is projected to reach 45 million by 2040, assuming current trends continue.
Immigration and Its Role
Immigration plays a pivotal role in shaping Canada's population. The country has a long history of welcoming newcomers, with policies designed to support economic growth and social cohesion. The Canadian government sets annual immigration targets, focusing on skilled workers, family reunification, and humanitarian cases.
Types of Immigrants
- Economic immigrants, including skilled workers and entrepreneurs.
- Family-class immigrants, who are sponsored by relatives already residing in Canada.
- Refugees and asylum seekers, who are granted protection due to persecution or conflict.
Statistics indicate that immigrants contribute significantly to Canada's workforce, with many settling in urban centers such as Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal.
Age Distribution
Canada's age distribution reflects an aging population, with a growing proportion of seniors. As of 2023, individuals aged 65 and above account for approximately 18% of the population. This trend is expected to continue, driven by advancements in healthcare and lower birth rates.
Impact of Aging Population
- Increased demand for healthcare services and retirement facilities.
- Potential strain on the workforce, as more individuals retire.
- Opportunities for innovation in senior care technologies and services.
To address these challenges, the Canadian government has implemented policies to support an aging population, including pension reforms and healthcare improvements.
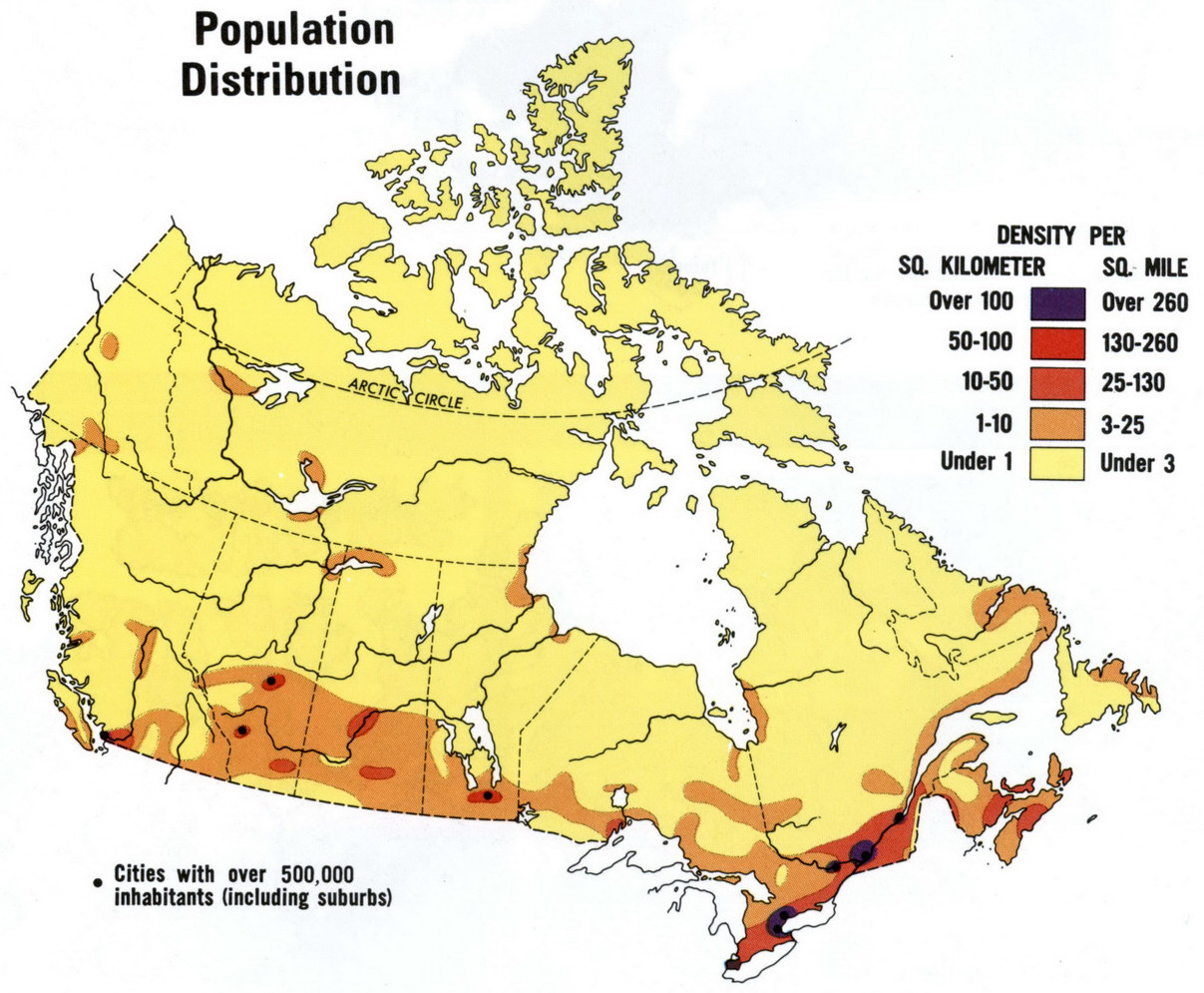
Regional Variation in Population
Canada's population is not evenly distributed across its provinces and territories. The majority of residents live in urban centers located in Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, and Alberta. These regions offer better economic opportunities, infrastructure, and services.
Provincial Breakdown
- Ontario accounts for approximately 39% of Canada's population.
- Quebec follows with around 23%, while British Columbia and Alberta each contribute about 13%.
- The territories and smaller provinces have significantly lower population densities.
This regional variation highlights the importance of addressing disparities in access to resources and services across the country.
Urbanization in Canada
Urbanization is a defining characteristic of Canada's population dynamics. Over 80% of Canadians live in urban areas, drawn by job opportunities, education, and cultural amenities. Major cities like Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal serve as hubs for economic activity and innovation.
Challenges of Urbanization
- Housing affordability remains a pressing issue in many urban centers.
- Traffic congestion and public transportation challenges need innovative solutions.
- Environmental sustainability must be prioritized to ensure urban areas remain livable.
Efforts to promote sustainable urban development are ongoing, with initiatives focusing on green spaces, renewable energy, and smart city technologies.
Economic Impact of Population Growth
Population growth has a profound impact on Canada's economy. A larger population translates into a bigger workforce, increased consumer spending, and enhanced innovation. However, managing this growth requires strategic planning and investment.
Key Economic Benefits
- Expansion of the labor market, attracting global talent.
- Increased demand for goods and services, boosting local economies.
- Enhanced competitiveness on the global stage, driven by innovation and diversity.
Despite these benefits, challenges such as infrastructure development and resource allocation must be addressed to ensure sustainable economic growth.
Challenges Facing Canada's Population
While Canada's population growth presents numerous opportunities, it also poses several challenges. Addressing these challenges is essential for maintaining the country's prosperity and quality of life.
Key Challenges
- Housing affordability and availability, particularly in urban areas.
- Access to healthcare services for remote and rural communities.
- Ensuring equal opportunities for all ethnic and cultural groups.
Policy measures and public-private partnerships are crucial for overcoming these obstacles and fostering inclusive growth.
Future Projections
Looking ahead, Canada's population is expected to continue growing, driven by immigration and natural increase. By 2050, the population could reach upwards of 50 million, depending on policy decisions and global trends.
Preparing for the Future
- Investing in infrastructure and services to accommodate population growth.
- Promoting innovation and technology to address emerging challenges.
- Encouraging sustainable development practices to protect the environment.
Canada's ability to adapt and innovate will be key to ensuring a prosperous and inclusive future for all its residents.
Conclusion
Canada's population is a vital component of its national identity and economic strength. From its diverse demographics to its steady growth patterns, the country's population dynamics reflect its commitment to inclusivity and progress. Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone interested in Canada's future development.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. Your feedback helps us improve and provide more valuable content. Additionally, consider exploring other articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of Canada and its many facets. Together, we can continue to celebrate the richness and diversity of this remarkable nation.