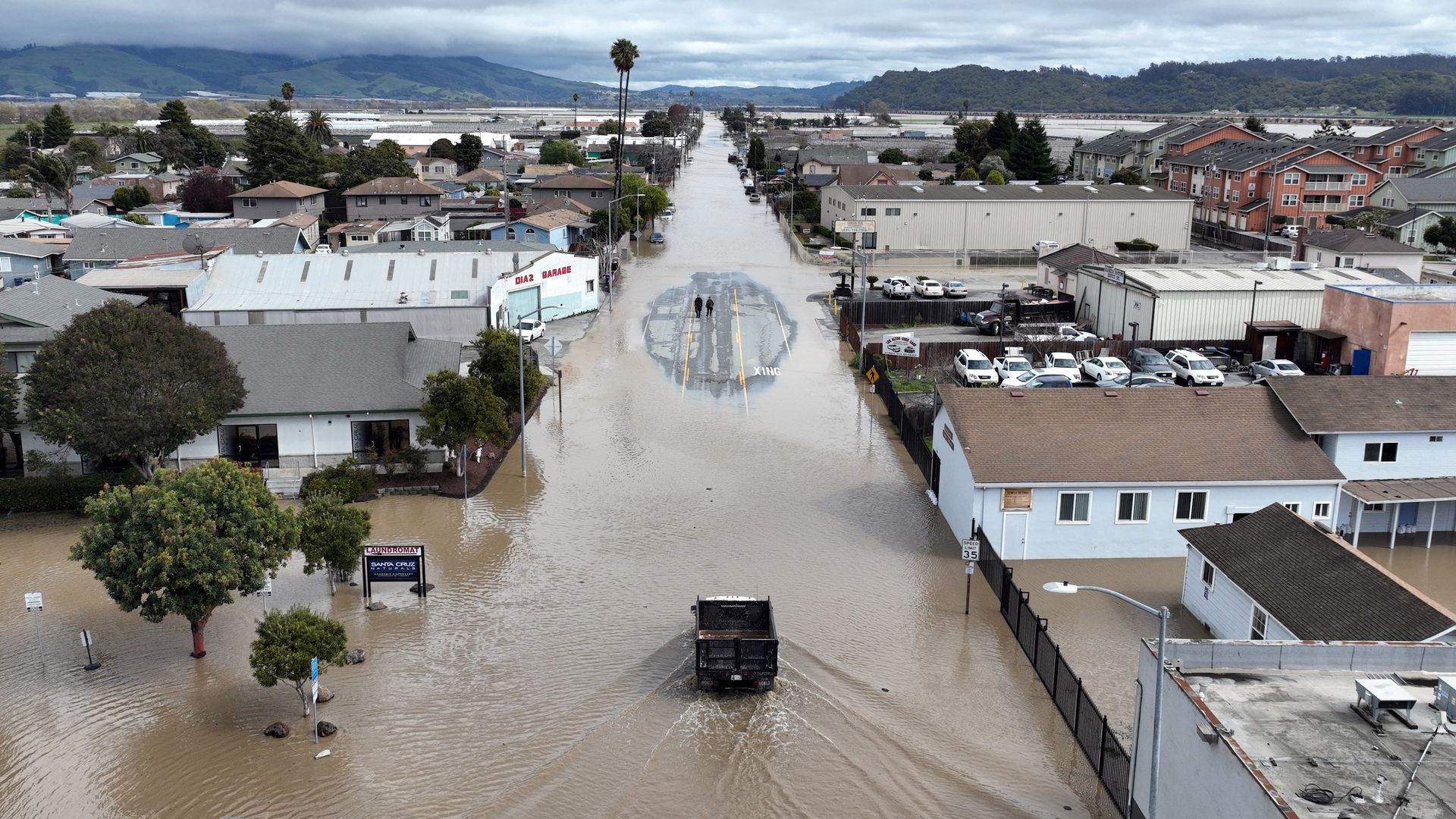
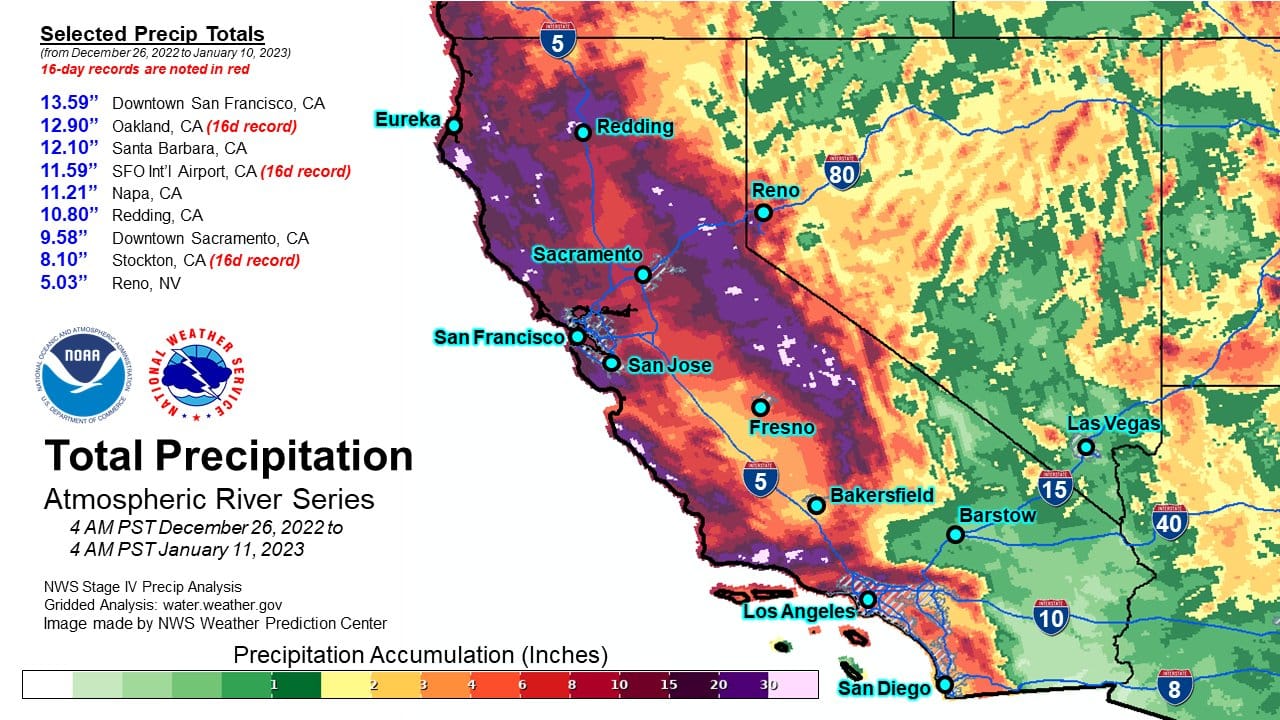
Atmospheric rivers in California have become increasingly significant meteorological phenomena, impacting weather patterns and water resources across the state. These powerful streams of moisture in the atmosphere can bring both beneficial rainfall and devastating floods. In recent years, California has experienced some of the most intense atmospheric river events, highlighting the importance of understanding their behavior and effects.
As climate change continues to reshape global weather patterns, atmospheric rivers are becoming more frequent and intense. This phenomenon is not only crucial for water supply management but also for disaster preparedness. By understanding how atmospheric rivers work, we can better prepare for their impacts and mitigate potential damage.
This article will explore the science behind atmospheric rivers, their effects on California, and strategies for managing their impacts. Whether you're a scientist, policymaker, or simply someone interested in weather patterns, this guide will provide valuable insights into one of California's most critical weather phenomena.
Read also:What Sign Is November 27th Discover Your Zodiac Sign And Personality Traits
What Are Atmospheric Rivers?
Atmospheric rivers (ARs) are narrow corridors of concentrated moisture in the atmosphere that transport water vapor from the tropics to higher latitudes. These "rivers in the sky" can carry as much water as 25 Mississippi Rivers combined, making them one of the most powerful forces in Earth's weather system.
ARs typically form when strong winds in the lower atmosphere draw moisture from warm ocean regions toward land. Once they reach land, this moisture can condense into rain or snow, leading to significant precipitation events. While ARs are a natural part of Earth's water cycle, their intensity and frequency have been influenced by climate change.
Key Characteristics of Atmospheric Rivers
- Width: Atmospheric rivers can span 250 to 375 miles across.
- Length: They often stretch over 1,200 miles, connecting tropical moisture sources to mid-latitude regions.
- Moisture Content: ARs transport an average of 7.5 to 15 times the amount of water flowing through the Mississippi River at New Orleans.
- Duration: Most ARs last between 24 to 72 hours, though some can persist for longer periods.
Atmospheric River California: A Unique Case
California's unique geography makes it particularly susceptible to atmospheric river impacts. The state's coastal mountains and inland valleys create ideal conditions for ARs to deliver heavy rainfall and snowfall. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in California's water supply, contributing up to 50% of the state's annual precipitation in some regions.
However, the benefits of ARs are often accompanied by significant risks. Intense AR events can lead to flooding, landslides, and infrastructure damage, posing serious threats to communities across the state. Understanding the relationship between atmospheric rivers and California's climate is essential for effective water resource management and disaster preparedness.
Impact on California's Water Supply
Atmospheric rivers are a double-edged sword for California's water supply. On one hand, they provide much-needed precipitation during dry seasons, replenishing reservoirs and groundwater supplies. On the other hand, their unpredictability and intensity can overwhelm infrastructure, leading to water loss and environmental damage.
How Do Atmospheric Rivers Form?
The formation of atmospheric rivers involves a complex interplay of atmospheric conditions. It begins with the convergence of warm, moist air from tropical regions, driven by strong wind patterns. These moisture-laden air masses are then transported across the Pacific Ocean toward the western United States, where they encounter California's coastal mountains.
Read also:Discover The Best Of Hdhubcom Your Ultimate Guide To Entertainment
As the moisture-laden air rises over the mountains, it cools and condenses, releasing precipitation in the form of rain or snow. The intensity of the precipitation depends on various factors, including the strength of the AR, its duration, and local topography.
Factors Influencing Atmospheric River Intensity
- Sea Surface Temperatures: Warmer ocean temperatures increase evaporation, leading to more intense ARs.
- Wind Patterns: Stronger wind speeds can transport more moisture over greater distances.
- Topography: Mountainous regions enhance precipitation by forcing air to rise and cool.
- Climate Change: Rising global temperatures contribute to more frequent and intense AR events.
Atmospheric River California: Recent Events
In recent years, California has experienced several notable atmospheric river events. These events have highlighted both the benefits and challenges associated with ARs. For instance, the 2022-2023 winter season saw a series of intense ARs that brought record-breaking rainfall to the state, alleviating drought conditions while also causing widespread flooding.
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the frequency and intensity of ARs in California have increased over the past few decades. This trend is expected to continue as global temperatures rise, making it increasingly important to develop effective strategies for managing AR impacts.
Notable Atmospheric River Events in California
Some of the most significant AR events in California's recent history include:
- The 1997 Pineapple Express, which caused widespread flooding and damage across the state.
- The 2017 AR event that filled Northern California's reservoirs to capacity, helping to end a five-year drought.
- The 2023 series of ARs that brought record rainfall to Southern California, highlighting the need for improved flood management infrastructure.
Effects of Atmospheric Rivers on California's Ecosystems
Atmospheric rivers have both positive and negative impacts on California's ecosystems. On the positive side, they provide essential moisture to forests, grasslands, and wetlands, supporting biodiversity and ecosystem health. However, intense AR events can also cause ecological damage through flooding, erosion, and habitat destruction.
Additionally, the increasing frequency and intensity of ARs pose challenges for species adaptation. Native plants and animals may struggle to cope with rapid changes in precipitation patterns, while invasive species may thrive in altered environments.
Adapting Ecosystems to Changing AR Patterns
Conservation efforts in California are increasingly focused on helping ecosystems adapt to changing AR patterns. Strategies include:
- Restoring natural floodplains to absorb excess water.
- Protecting wetlands and riparian zones to enhance water storage capacity.
- Implementing climate-smart conservation practices to support species adaptation.
Atmospheric River California: Economic Impacts
The economic implications of atmospheric rivers in California are significant. While ARs contribute to the state's water supply, supporting agriculture and urban water needs, they also pose substantial risks to infrastructure and property. Flood damage from intense AR events can cost billions of dollars annually, impacting both public and private sectors.
Furthermore, the unpredictability of ARs complicates water resource management, leading to challenges in balancing water storage and flood control. As the frequency and intensity of ARs increase, so too does the need for investment in resilient infrastructure and disaster preparedness.
Managing Economic Risks from Atmospheric Rivers
Effective risk management strategies for AR impacts include:
- Investing in flood control infrastructure, such as levees and floodgates.
- Developing early warning systems to improve disaster preparedness.
- Implementing water conservation measures to optimize resource use.
Scientific Research on Atmospheric Rivers
Advances in scientific research have significantly improved our understanding of atmospheric rivers. Satellite technology, atmospheric models, and ground-based observations provide valuable insights into AR formation, behavior, and impacts. This research is essential for developing effective forecasting tools and management strategies.
For example, the California-Nevada Applications Program (CNAP) works closely with NOAA to monitor AR activity and provide real-time data to decision-makers. These efforts have led to improved forecast accuracy and enhanced disaster preparedness across the state.
Key Findings from Atmospheric River Research
- ARs contribute up to 40% of California's annual precipitation.
- Climate models predict a 50% increase in AR frequency by the end of the century.
- Warmer temperatures are likely to increase AR moisture content by 10-20%.
Atmospheric River California: Future Challenges
As climate change continues to alter atmospheric conditions, the challenges posed by atmospheric rivers in California are expected to grow. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased variability in weather systems all contribute to a more uncertain future for water resource management and disaster preparedness.
Addressing these challenges will require coordinated efforts across government agencies, research institutions, and local communities. By investing in resilient infrastructure, improving forecasting capabilities, and implementing adaptive management strategies, California can better prepare for the impacts of atmospheric rivers in the years to come.
Strategies for Addressing Future AR Challenges
Potential strategies for managing future AR impacts include:
- Expanding water storage capacity through new reservoirs and groundwater banking.
- Enhancing flood control infrastructure to protect vulnerable communities.
- Developing climate-resilient agricultural practices to optimize water use.
Conclusion
Atmospheric rivers in California represent both an opportunity and a challenge for water resource management and disaster preparedness. While these powerful weather phenomena provide essential moisture to the state, their increasing frequency and intensity pose significant risks to communities and ecosystems. By understanding the science behind atmospheric rivers and implementing effective management strategies, California can better prepare for their impacts and harness their benefits.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with atmospheric rivers in the comments below. For more information on this topic, explore our related articles on climate change and water resource management. Together, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable future for California.
Table of Contents
- What Are Atmospheric Rivers?
- Atmospheric River California: A Unique Case
- How Do Atmospheric Rivers Form?
- Atmospheric River California: Recent Events
- Effects of Atmospheric Rivers on California's Ecosystems
- Atmospheric River California: Economic Impacts
- Scientific Research on Atmospheric Rivers
- Atmospheric River California: Future Challenges
- Conclusion