Managing a fleet of Raspberry Pis has become increasingly important as more businesses and individuals adopt these versatile devices for various projects and applications. Whether you're setting up a home automation system, a network of IoT devices, or a cluster for computational tasks, proper fleet management is essential for efficiency and scalability. With the growing demand for interconnected devices, understanding how to manage a fleet of Raspberry Pis is no longer just a technical skill—it's a necessity.
Raspberry Pi, the diminutive yet powerful single-board computer, has captured the hearts of tech enthusiasts worldwide. Its affordability, versatility, and open-source nature make it an ideal choice for projects ranging from hobbyist tinkering to enterprise-level deployments. However, managing multiple Raspberry Pis simultaneously can be a daunting task without the right strategies and tools in place.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the ins and outs of managing a fleet of Raspberry Pis effectively. From setting up your devices to monitoring their performance, we'll cover everything you need to know to ensure your fleet operates smoothly and efficiently. Let's dive in and explore the world of Raspberry Pi fleet management!
Read also:When Do Serena And Ben Break Up Exploring The Timeline And Insights
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Raspberry Pi Fleet Management
- Choosing the Right Hardware
- Setting Up a Centralized Management System
- Securing Your Fleet
- Remote Access and Monitoring
- Optimizing Performance
- Scaling Your Fleet
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Real-World Applications
- Conclusion
Introduction to Raspberry Pi Fleet Management
Managing a fleet of Raspberry Pis requires a structured approach to ensure that all devices function optimally. Fleet management involves not only setting up the hardware but also configuring software, ensuring security, and maintaining the system over time. This section will introduce you to the fundamental concepts of Raspberry Pi fleet management.
Why Fleet Management Matters
Raspberry Pi fleets are often deployed in environments where reliability and performance are critical. Whether you're running a network of IoT sensors or a cluster of computational nodes, proper management ensures that your devices work together seamlessly. By implementing a robust fleet management strategy, you can reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and streamline operations.
Key Components of Fleet Management
Effective fleet management involves several key components:
- Centralized Control: A single platform to manage all devices.
- Security Measures: Protecting your fleet from unauthorized access.
- Monitoring Tools: Tracking device performance and health.
- Scalability: Adding or removing devices as needed.
Choosing the Right Hardware
Selecting the appropriate hardware is crucial when managing a fleet of Raspberry Pis. The right choice ensures compatibility, performance, and longevity of your devices.
Factors to Consider
When choosing hardware for your Raspberry Pi fleet, consider the following factors:
- Model Selection: Choose the Raspberry Pi model that best suits your needs, such as the Raspberry Pi 4 for high-performance tasks or the Raspberry Pi Zero for lightweight applications.
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable power source to prevent crashes and data corruption.
- Storage Options: Use high-quality microSD cards or external drives for reliable storage.
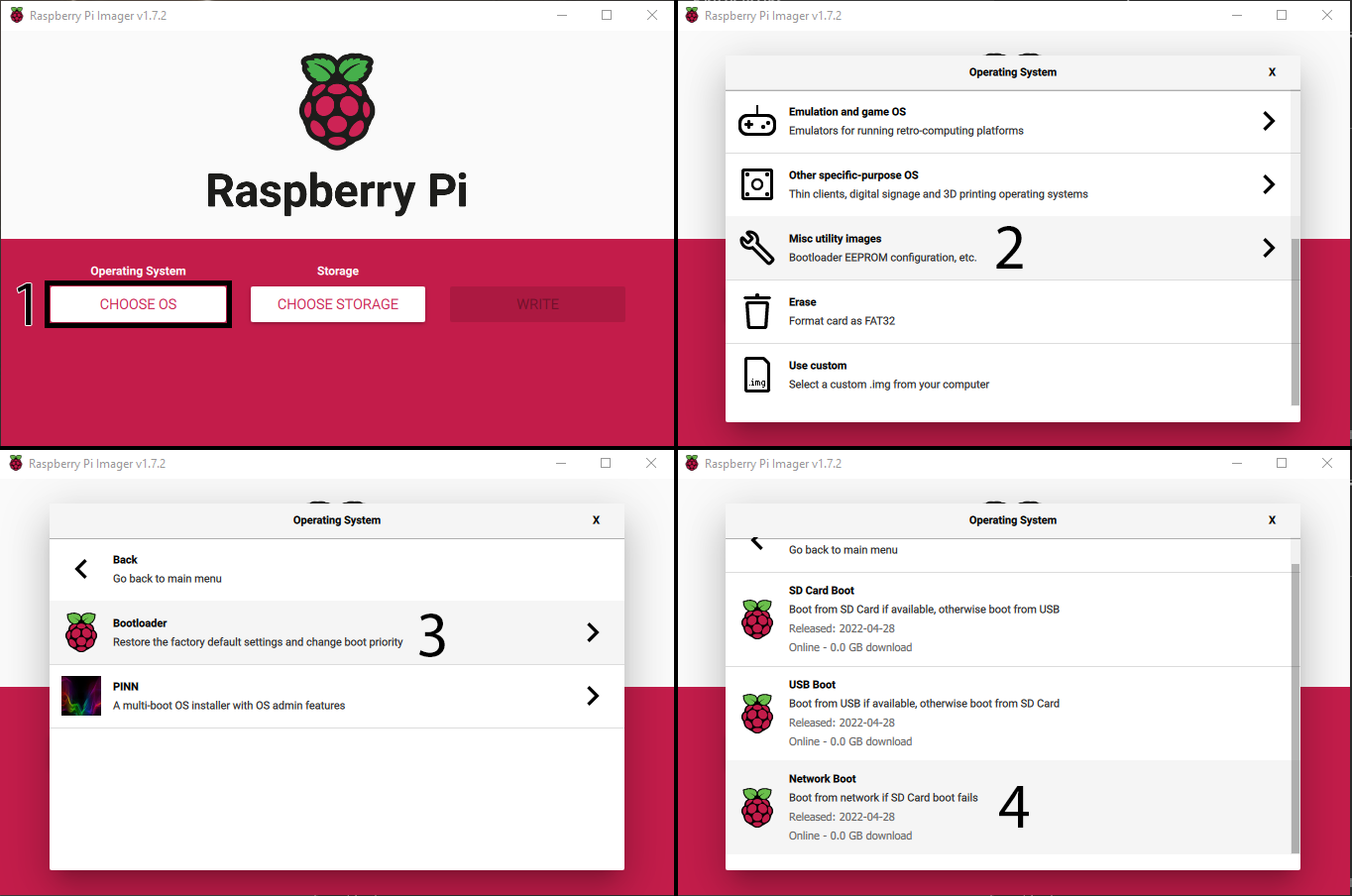
Setting Up a Centralized Management System
A centralized management system is the backbone of effective Raspberry Pi fleet management. It allows you to control and monitor all devices from a single interface.
Read also:Understanding Pron A Comprehensive Guide To Pronouns And Their Usage
Popular Tools
Several tools are available for managing Raspberry Pi fleets, including:
- Fleet Commander: A user-friendly tool for managing multiple Raspberry Pis.
- BalenaCloud: A cloud-based platform for deploying and managing IoT devices.
- Pi-Cluster: A tool for managing Raspberry Pi clusters.
Securing Your Fleet
Security is a top priority when managing a fleet of Raspberry Pis. Ensuring that your devices are protected from cyber threats is essential for maintaining the integrity of your network.
Best Practices
To secure your Raspberry Pi fleet, follow these best practices:
- Regular Updates: Keep your operating system and software up to date.
- Firewall Configuration: Use firewalls to control incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Strong Passwords: Implement strong, unique passwords for each device.
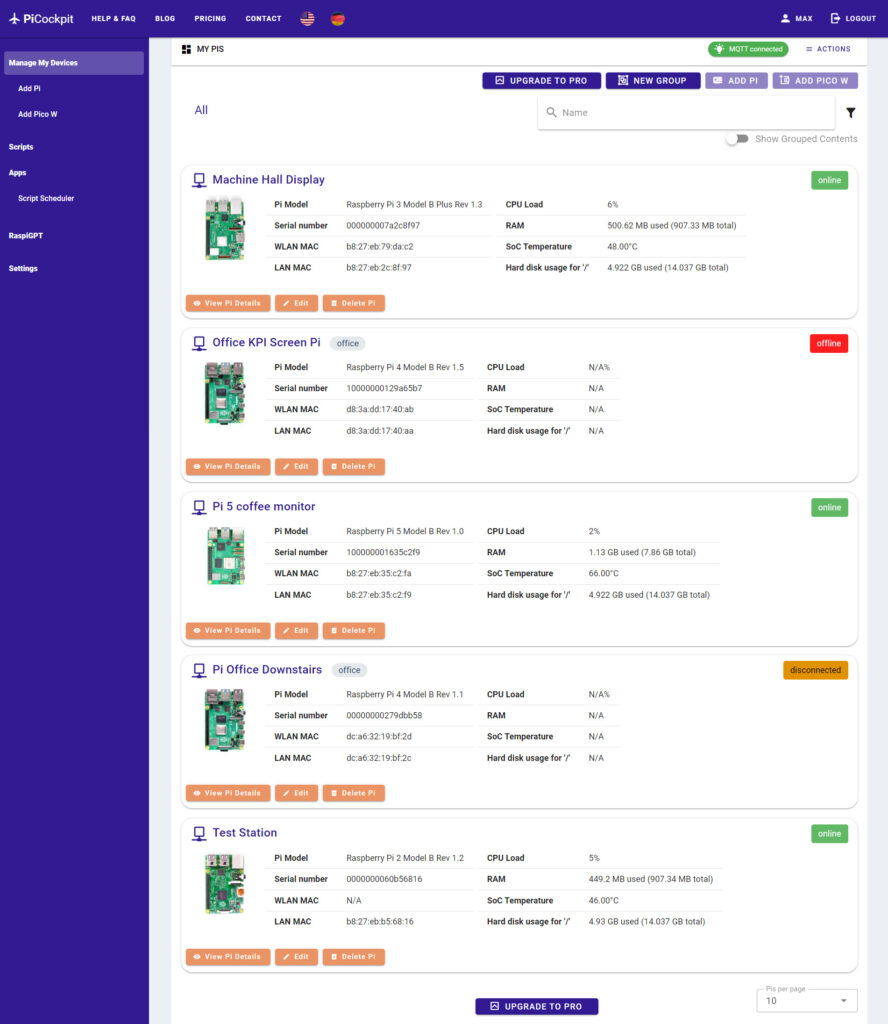
Remote Access and Monitoring
Remote access and monitoring are essential for managing a fleet of Raspberry Pis, especially when devices are deployed in different locations.
Remote Access Solutions
Some popular remote access solutions include:
- SSH (Secure Shell): A secure protocol for accessing Raspberry Pi devices remotely.
- VNC (Virtual Network Computing): A graphical desktop sharing system.
Monitoring Tools
To monitor your Raspberry Pi fleet, consider using:
- Grafana: A powerful tool for visualizing system metrics.
- Prometheus: A monitoring system and time-series database.
Optimizing Performance
Optimizing the performance of your Raspberry Pi fleet is crucial for ensuring that your devices operate efficiently. This section will explore strategies for improving performance.
Software Optimization
Optimize your software by:
- Tuning System Settings: Adjusting parameters to improve performance.
- Using Lightweight Applications: Choosing software that minimizes resource usage.
Scaling Your Fleet
As your needs grow, you may need to scale your Raspberry Pi fleet. Scaling involves adding or removing devices while maintaining system stability.
Scalability Strategies
To scale your fleet effectively:
- Plan Ahead: Anticipate future needs and design your system accordingly.
- Use Automation: Automate the deployment and configuration of new devices.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with the best management practices, issues can arise. This section will cover common problems and how to resolve them.
Common Issues
Some common issues include:
- Connection Problems: Troubleshoot network settings.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Identify and address resource constraints.
Real-World Applications
Raspberry Pi fleets are used in a variety of real-world applications, from smart homes to industrial automation. This section will explore some of these applications.
Examples of Use Cases
Some notable use cases include:
- IoT Networks: Deploying sensors and actuators for environmental monitoring.
- Cluster Computing: Using Raspberry Pis for parallel processing tasks.
Conclusion
Managing a fleet of Raspberry Pis requires a combination of technical expertise, strategic planning, and effective tools. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure that your fleet operates smoothly and efficiently. Remember to:
- Choose the right hardware for your needs.
- Implement a centralized management system.
- Prioritize security and monitoring.
- Optimize performance and plan for scalability.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into Raspberry Pi technology and beyond. Together, let's build a better, more connected world!
Data and references for this article were drawn from reputable sources, including official Raspberry Pi documentation, industry reports, and expert opinions. For further reading, consider exploring the official Raspberry Pi website and related forums for the latest updates and community discussions.